Whether it is sound, vibrations or electromagnetic radiation, with smart monitoring we can acquire more information from measurements. Through the usage of machine learning algorithms and physics-based modeling, measurements can provide better insight than the data by itself. These insights lead to detailed prognoses and consulting services.
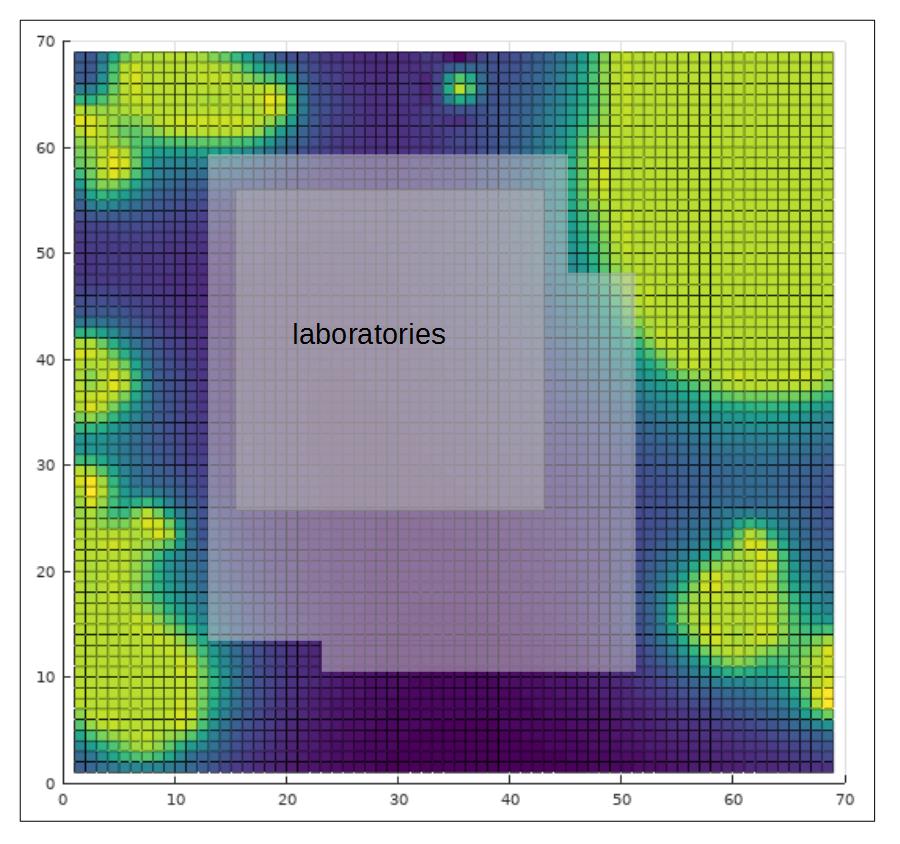
An example is an investigation of the levels of electromagnetic radiation at the location of a planned building with laboratories where work with high sensitivity to EM radiation will be carried out. At a number of specific positions measurements are carried out to determine the occurring levels due to several sources of EM-radiation, like a nearby transformer, ground pumps and power lines in the ground. The EM-radiation levels in the project area are made visible with a combination of measurement data, a physics-based model and a machine learning algorithm. Based on this detailed EM-radiation level map the client is consulted on the best location for the planned laboratories.
A system that allows us to monitor sound and/or vibrations on several locations in an area of study without the necessity of having measurement equipment at all locations during the whole monitoring duration is also a good example of smart monitoring. Relations in the measurement data can be utilized through the use of machine learning algorithms, so that with less measurement equipment more information becomes available.
With this integral approach of machine learning, physics-based modeling and measurements detailed prognoses can be made. Because of this, smart monitoring can provide insights that can lead to better decisions in the areas of building, industry, environment and energy and sustainability. Feel free to contact us when you would like to know more.